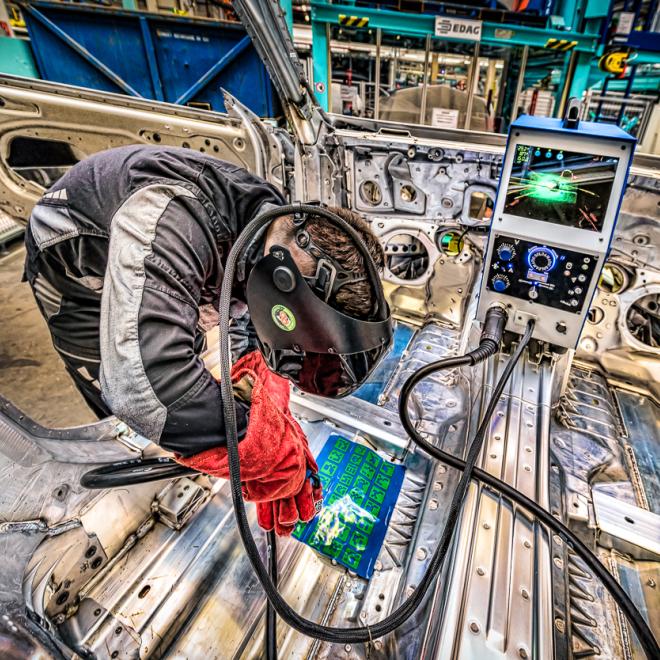

The role
Tasks include:
• blueprint reading
• metal fabrication
• cutting and welding.

Skills required to be a Rollingstock Welder
- Attention to detail
- Steady hands and good hand-eye coordination
- Ability to learn new things
- Physical strength and endurance
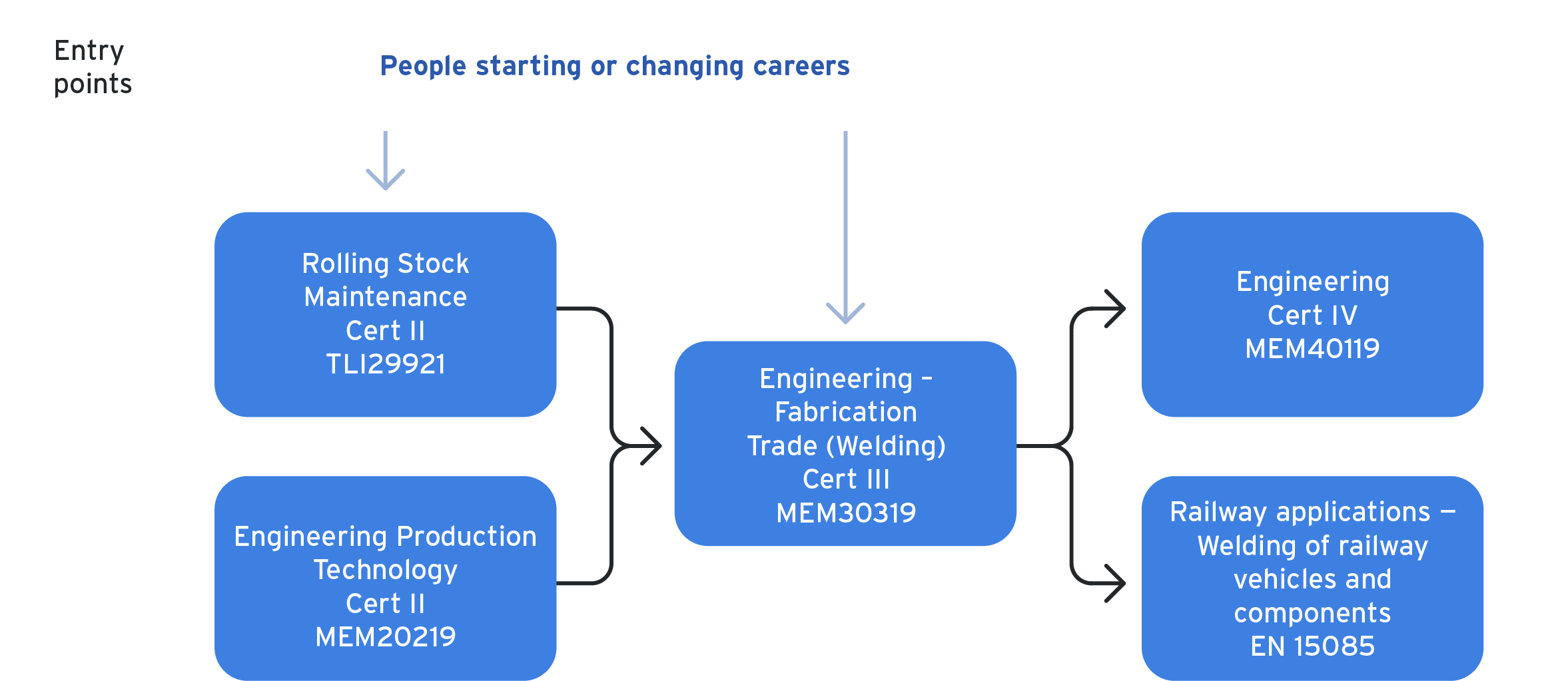
Entry requirements
The minimum mandatory qualification for a Rollingstock Welder is MEM30319 - Certificate III in Engineering - Fabrication Trade (Welding). This is usually completed as part of an apprenticeship to become a fully qualified welder.
However, many rolling stock manufacturers and repairers require additional international certification such as EN 15085. This sets higher standards and protects the reliability of rollingstock. The EN 15085 requires the certification of the individual welder, their company and welding processes.
AS/NZS ISO 9606-1 is the standard used to certify welders to a specific welding procedure.
Individual welders may have multiple welder certifications, each can last for up to 3 years.
Optional additional qualifications: MEM40119 - Certificate IV in Engineering.
Alternative entry points: MEM20219 - Certificate II in Engineering - Production Technology or MEM10119 - Certificate I in Engineering.
Few people enrol in the Certification II qualification, however a number of elective units in this course can be used as a credit transfer to the Certification III welding qualification.
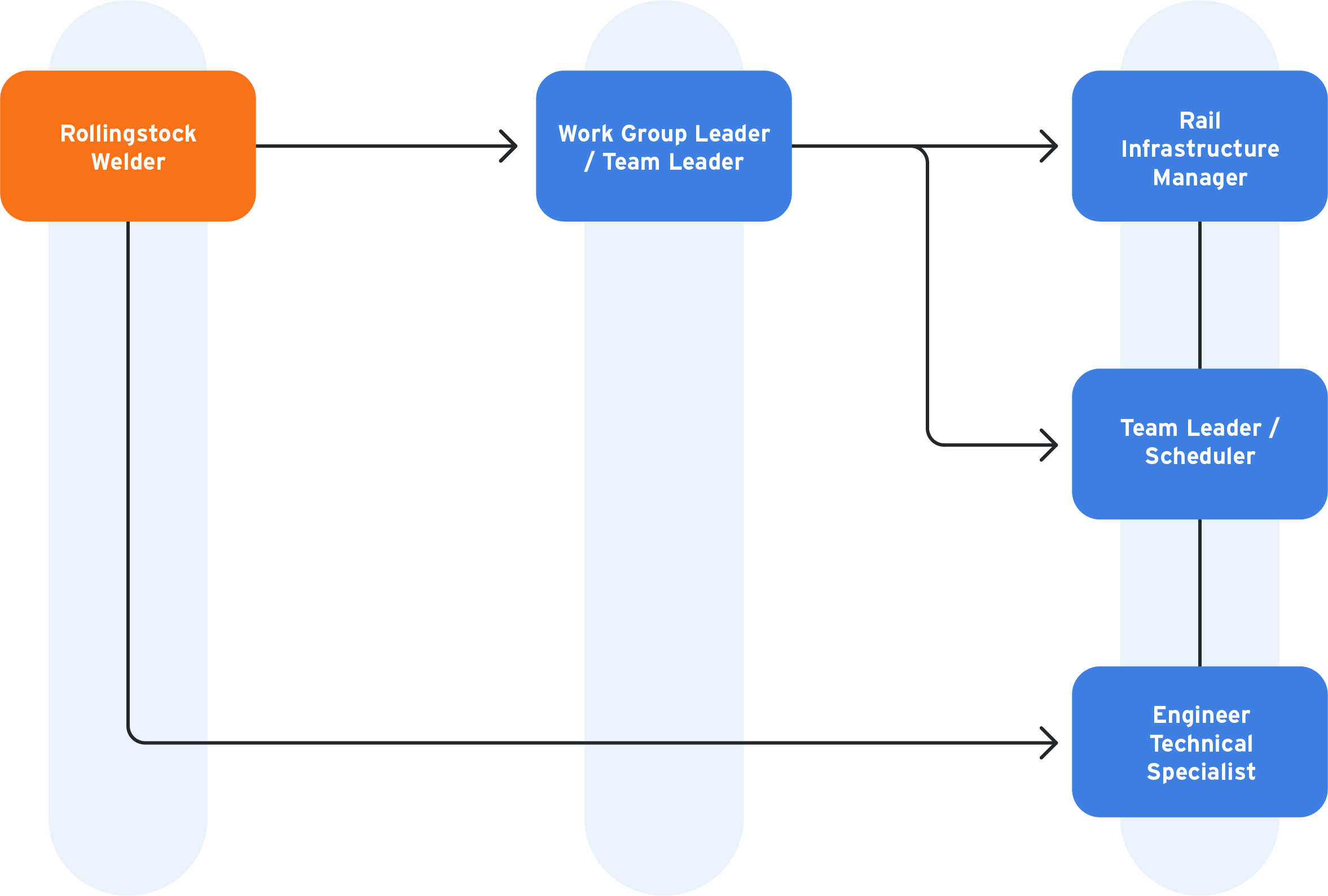
Potential training pathway
What a Rollingstock Welder's career progression can look like
Rollingstock welders may look to advance their career by moving into roles such as work group or team leader, engineer technical specialist or in logistics or rail infrastructure.
What do I do next?
Our findings include information from the Australian Industry Standards. See their full rollingstock welder pathway here.
For more information about becoming a Rollingstock Welder:
- check out the Sheet Metal Worker page on the Work in Rail website
- talk to your careers adviser
- get in touch with Weld Australia
- if you already work in rail, talk to your employer
